Quick Turn PCB Circuit Board Prototype Assembly

Quickest 24h Quick-Turn with Highest Quality
About Circuit Board Prototype:
PCB prototype board assembly involves creating a small-scale version of a printed circuit board (PCB) design for testing, evaluation, and validation before mass production. This prototype, also known as PCBA, provides a functional model to verify if it operates as intended.
Quick Turn Circuit Board Assembly is a vital step in quick time to market of your products, our quickes turn is as Quick as within 24 Hours.
Key Benefits of PCB Prototyping
- Engineers can test the circuitry and validate the layout before mass production.
- Potential issues can be identified early, allowing for design improvements.
- Our free Design for Manufacturability (DFM) review services can assess component availability, lead times, costs, and substitutions to ensure smooth production.
Over 30 Years of Experience and Proven Expertise

Our SVP of Engineering and Manufacturing brings over 30 years of experience in the electronics contract manufacturing industry. They have been a pioneer in quick-turn PCB (Printed Circuit Board) prototyping and New Product Introduction (NPI), previously leading global NPI operations at Finepitch and Solectron. Their expertise ensures the seamless integration of new products into manufacturing, a key factor in accelerating time-to-market for innovative electronic products.
Thanks to the wealth of best practices they have developed, we are recognized as leaders in quick-turn PCB prototyping and NPI. Our Quality and efficiency have earned us as the preferred quick-turn PCB prototype assembly partner for engineers across Silicon Valley, the global hub of technological innovation.
Our SVP of Engineering is a Ph.D. in mechanical engineering from Pan State University; he is also a qualified IPC instructor, and he provides frequent professional training for our team.
Contact us today for a free consultation on how we can help bring your products to market faster.
The process of Prototype PCB assembly
- PCB Fabrication: The design files (Gerber files) are used to manufacture the bare PCB according to the specified design. This involves printing the circuitry on the board and etching away excess copper.
- Component Procurement: Sourcing electronic components required for the prototype assembly. This involves purchasing the necessary integrated circuits, resistors, capacitors, connectors, etc., as specified in the bill of materials (BOM).
- Stencil Creation: A solder paste stencil is created based on the PCB design to apply solder paste accurately onto the PCB pads.
- Component Placement: Automated or manual placement of the electronic components onto the PCB. Pick-and-place machines are often used in automated assembly to precisely position components according to the design.
- Soldering: Solder paste, which is a mixture of tiny solder balls and flux, is applied to the PCB pads. Then, the components are carefully placed on the solder paste. The PCB is heated in a reflow oven, melting the solder to establish electrical connections between the components and the board.
- Inspection:After soldering, the assembled PCB undergoes visual inspection and testing to ensure the components are correctly placed, soldered, and that there are no defects.
- Functional Testing: Testing the assembled prototype to verify its functionality and performance. This might involve powering up the PCB and testing its various functions or interfaces.
- Debugging and Iteration:If any issues are found during testing, debugging and necessary modifications or revisions to the design are made. This iterative process continues until the prototype meets the required specifications and functions as intended.
Prototype PCB assembly is very important for reducing the risk and cost associated with potential design flaws. It is mission-critical for speeding up the "Time-to-Market" and the success of your new product introduction, and it is crucial to have a competent and trustworthy EMS partner. Try us, and you will find that Sparqtron can far exceed both other EMS vendors performance and your expectations.
Quick-Turn PCBA Prototype
Assembly Services (< 24 hours)
Quick turn prototype assembly refers to the rapid production of small quantities of PCB prototype boards for testing and validating designs in a short timeframe, typically within 24 to 48 hours. Below is the process for Quick-Turn PCBA Prototype Assembly:

We understand the urgency of any quick prototype build, our quick-turn PCBA prototyping process delivers a finished product in as little as 24 hours, and our engineers are always receptive and flexible to the wide range of dynamic requirements you may have, such as the last moment engineering change. We even support the engineer change on-the-go if possible. Our consistent quality performance and on-time delivery promises to dramatically reduce the time-to-market of your upcoming new product.
Feel free to contact us to know how easy to work with us.
Customer Satisfaction
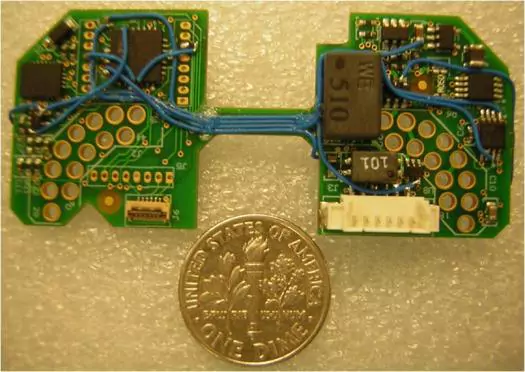
Success Story of Rapid Prototype Reworking:
The entire engineering team expressed their heartfelt gratitude, acknowledging that failure at this event could have led to the team’s dissolution.
Through the entire PCBA prototype and NPI process, Sparqtron has consistently provided on-time deliveries that exceed our customers' quality, speed, and service expectations. We frequently receive customer appreciations for our level of quality and service in helping them launching new products swiftly to market at lowest total cost.
We are one of best PCB Prototype Board Assembly and NPI manufacturer of choice, we are located in Bay Area, Silicon Valley, California, USA. (Near by San Jose)
PCB Prototype Assembly Q&A
Please click the question to get the answer.
Why is testing important in PCB prototype assembly?
Testing ensures the functionality and reliability of the assembled PCB, helping to identify issues before mass production.
What are some common testing methods used in PCB assembly?
Common methods include visual inspection, automated optical inspection (AOI), in-circuit testing (ICT), functional testing, and boundary scan testing.
How can errors in PCB assembly be rectified?
Errors can be fixed through rework, which includes replacing faulty components, re-soldering connections, or making necessary adjustments.
What are the benefits of PCB prototype assembly?
PCB prototype assembly helps in validating design, detecting errors early, reducing risks, improving quality, and allowing modifications before mass production.
What factors should be considered when choosing components for PCB assembly?
Considerations include availability, cost, reliability, voltage and temperature ratings, and compatibility with the manufacturing process.
How crucial is design for manufacturability (DFM) in PCB prototype assembly?
DFM is essential to optimize design for cost-effective and error-free manufacturing, reducing complications during assembly.
How can thermal considerations be managed in PCB prototype assembly?
Proper component placement, adequate spacing, thermal vias, heat sinks, and selecting suitable components help manage thermal issues.
What role does quality control play in PCB prototype assembly?
Quality control ensures that the PCB meets standards, involving inspections, testing, and adherence to quality assurance procedures.
What are the considerations for selecting a PCB assembly manufacturer?
Factors include experience, capabilities, certifications, production capacity, quality standards, lead times, and cost-effectiveness.
Is it possible to iterate and modify a PCB prototype after assembly?
Yes, PCB prototypes can be reworked by replacing components, making design adjustments, or incorporating feedback from testing.
How important is component compatibility in PCB assembly, and what are the considerations for substitution?
Compatibility is crucial. Substitutions must match electrical characteristics, package type, temperature range, and form factor.
What role does design validation play in PCB prototype assembly, and how is it typically performed?
Design validation ensures performance and reliability. It involves simulations, prototyping, testing, and analysis before production.
How can cost-effectiveness be achieved in PCB prototype assembly without compromising quality?
Optimizing manufacturing processes, careful component selection, reducing material waste, and streamlining workflows help control costs.
What considerations should be made regarding variations in material availability, lead time, and cost during PCB assembly?
Strategies include maintaining supplier relationships, forecasting needs, and contingency planning for alternative sourcing.
Top Choice for PCB Prototype Assembly Vendor
with Oustanding Engineering & Manfacturing Support
Top



